Deformation and Elastic Behaviour of Solids
Deformation and Elastic Behaviour of Solids: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as elasticity, deforming force, plastic body, internal restoring force, and elastic deformation.
Important Questions on Deformation and Elastic Behaviour of Solids
Why does a rubber band become loose after repeated use?
A mode of fracture that is attended by extensive plastic deformation is called
For small deformations, the stress and strain are proportional to each other. What is this known as
Fully recoverable but time-dependent deformation is known as:
What are the types of deformation
When is a body said to be perfectly elastic
If the material recovers the original dimensions, when an external load is removed, this deformation is known as ______ deformation.
What is Plasticity?
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
A wire is suspended vertically from a rigid support. When loaded with a body in air, the wire extends by and when the body is immersed completely in water, the extension is reduced to . The relative density of material of the body is
Distinguish between elasticity and plasticity.
An uniform steel rod of cross section is heated from to . Find the force which must be exerted to prevent it from expanding.
Explain the term: perfectly plastic body
Explain the term: perfectly elastic body.
What do you mean by elastic bodies and plastic bodies?
Explain the concept of elasticity.
Two wires are made of the same material and have the same volume. However, wire has cross-sectional area and wire has cross-sectional area . lf the length of wire increases by on applying force , then how much force is needed to stretch wire by the same amount?
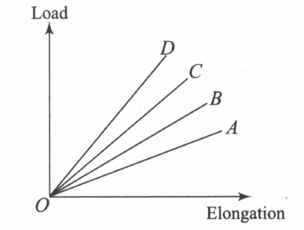
The load versus elongation graph for four wires of the same material is shown in the figure. The thinnest wire is represented by the line
A steel wire is suspended vertically from a rigid support. When loaded with a weight in air, it expands by and when the weight is immersed completely in water, the extension is reduced to . Then relative density of the material of the weight is
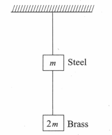
If and are the ratio of lengths, radii and Young's moduli of steel and brass wires in the above figure, find the corresponding ratio of increase in their lengths.
